Graphene Membrane/Graphite
Mechanical Properties - Nanoindentation
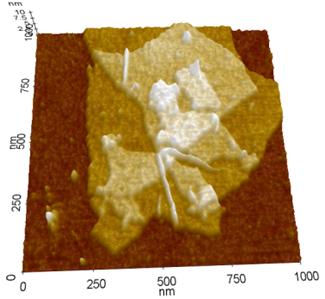
Graphite is a layered compound composed of carbon atoms. It is important industrially for its electrical and lubricating properties. Graphite is made up of layers of graphene, which is thought to be on of the strongest materials to be tested with a breaking strength 200 times that of steel.
Relevant Publication using the Park AFM and Nanoindentation
Title: Measurement of the Elastic Properties and Intrinsic Strength of Monolayer Graphene
Authors: C. Lee, X.Wei, J.W. Kysar, J. Hone
Journal: SCIENCE 321(18) JULY 2008 p. 385
System: Park Systems XE-100
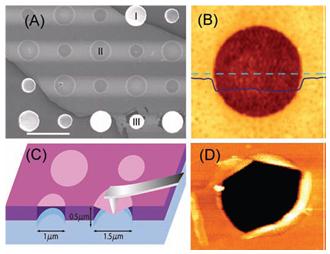
We measured the elastic properties and intrinsic breaking strength of free-standing monolayer graphene membranes by nanoindentation in an atomic force microscope. The force-displacement behavior is interpreted within a framework of nonlinear elastic stress-strain response, and yields second- and third-order elastic stiffnesses of 340 newtons per meter (N m-1) and -690 N m-1, respectively. The breaking strength is 42 N m-1 and represents the intrinsic strength of a defect-free sheet. These quantities correspond to a Young’s modulus of E = 1.0 terapascals, third-order elastic stiffness of D = –2.0 terapascals, and intrinsic strength of sint = 130 gigapascals for bulk graphite. These experiments establish graphene as the strongest material ever measured, and show that atomically perfect nanoscale materials can be mechanically tested to deformations well beyond the linear regime.
